问题备注
- 常识用于回答生成式多跳阅读理解
- 阅读理解
- 给一个文本片段和一个问题,给出问题的答案
摘要贡献
- multihop generative task (NarrativeQA), 多跳生成式任务
-
推理、聚合、同步上下文中不同的信息,然后生成答案。这种推理能理解隐含的关系,而人类是通过外部的、背景常识做到。
- 一个强的生成式baseline——multi-attention模型,用于实现多跳推理;以及pointer-generator decoder模型,用于合成答案。
- 然后介绍了一个用于从ConceptNet中抽取多跳关系常识信息的system,方法是引入了一个评分函数(pointwise mutual information + term-frequency )。
-
最后有效的利用提取的常识信息填补上下文的推理中(selectively-gated attention mechanism)
- 机器语言理解(MRC)通过这个来做QA
- 该任务,通过基于相关内容的问题回答,检测了一个模型的自然语言理解捕获能力
# 已有的进展以及存在的问题
- bAbI dataset:和human-generated text相比,文章结构简单,含有的词汇也少;
- CNN/DM (Hermann et al.,2015) and SQuAD (Rajpurkar et al., 2016) : 基于事实,并且没有将问题放在多跳推理问题上。
- QAngaroo: 聚焦于长文本上, 答案中的词都局限于当前的content中, 因此不能够综合和生成新的信息。
方法
- NarrativeQA generative dataset:基于该数据集, 包含的问题中,文本比较长,故事比较复杂,因此仅仅是聚合事实和无法生成新的信息的模型是不够的。因此之前在其他数据集上较好的, 在该数据集上会受到限制。
- 首先提出了MHPGM模型
模型
Multi-Hop Pointer-Generator Model(MHPGM),
-
一个强的baseline, 使用双向attention, self-attention, and a pointer-generator。
-
可以有效地在一篇长文本中,进行阅读和推理, 然后人工合成一个统一的应答。
-
our model achieves 41.49 rouge-l and 17.33 meteor on the summary subtask of NarrativeQA, substantially better than the performance of previous generative models.
在叙事学的总结子任务上,我们的模型获得了41.49颗胭脂-l和17.33颗流星,本质上比以往的生成模型的性能要好得多。
-
next, to address the issue that understanding human-generated text and performing longdistance reasoning on it often involves intermittent access to missing hops of external commonsense (background) knowledge, we present an algorithm for selecting useful, grounded multi-hop relational knowledge paths from conceptnet (speer and havasi, 2012) via a pointwise mutual information (pmi) and term-frequency-based scoring function.
接下来,为了解决理解人工生成的文本并对其执行长距离推理常常涉及对外部常识(背景)知识的缺失跳数的间歇访问的问题,我们提出了一种算法,通过点态互信息(Pmi)和基于词频的评分函数,从ConceptNet(Speer和havasi,2012)中选择有用的、接地的多跳关系知识路径。
-
we then present a novel method of inserting these selected commonsense paths between the hops of document-context reasoning within our model, via the necessary and optional information cell (noic), which employs a selectivelygated attention mechanism that utilizes commonsense information to effectively fill in gaps of inference. with these additions, we further improve performance on the narrativeqa dataset, achieving 44.16 rouge-l and 19.03 meteor (also verified via human evaluation). we also provide manual analysis on the effectiveness of our commonsense selection algorithm
然后,我们提出了一种新的方法,通过必要的和可选的信息单元(Noic)在文档上下文推理的跃点之间插入这些选定的常识路径,该机制采用了选择性的注意机制,利用常识信息有效地填补了推理的空白。通过这些添加,我们进一步提高了叙事QA数据集的性能,达到了44.16 Rouge-l和19.03流星(也是通过人类评估验证的)。我们还对我们的常识选择算法的有效性进行了手工分析。
-
finally, to show the generalizability of our multi-hop reasoning and commonsense methods, we show some promising initial results via the addition of commonsense information over the baseline on qangaroo-wikihop (welbl et al., 2018), an extractive dataset for multi-hop reasoning from a different domain
最后,为了展示我们的多跳推理和常识方法的通用性,我们通过在qangaroo-wikihop(Welbl等人,2018)的基线上添加常识信息,展示了一些有希望的初步结果。qangaroo-wikihop是一个针对不同领域的多跳推理的抽取数据集。
模型解读

baseline
-
严格定义了QA问题
-
给定两个输入引用的序列;
背景向量context:Xc = {w1c, w2c, …., wnc}
问题向量query:XQ = {w1Q, w2Q, …, WmQ}
系统应该生成回答引用Xa = {w1q, w2q, …,wpa}
embedding layer
-
这些标记为嵌入到学习到的词向量learned word embeddings,以及预训练好的背景意识词向量pretrained context-aware embeddings (ELMo)
-
we embed each word from the context and question with a learned embedding space of dimension d
我们将上下文和问句中的每个单词嵌入到一个学习的d维嵌入空间中。
-
从1024维的预训练语言模型(ELMo)中获取上下文词向量
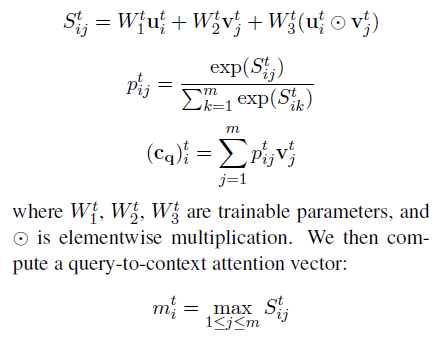
reasoning layer
- 嵌入的上下文通过k个推理单元reasoning cell进行传递
- 通过BiDAF attention 从查询中的信息,更新上下文表示context representation
- 通过多步骤推理过程, 计算一个单独的推理步骤
- 使用双向LSTM

-
emulate a hop of reasoning by focusing on relevant aspects of the context
通过专注于上下文的相关方面来模仿推理的跳跃。
-
计算context-to-query attention
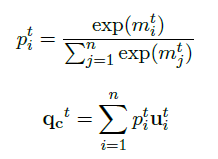

-
elementwise multiplication
元素乘法
ct: cell的输出
-
最开始推理层的输入是嵌入的context representation, 比如 c0 = eC
-
最终推理层的输出是last cell , ck
self-attention layer
-
the context representation is passed through a layer of self-attention (cheng et al., 2016) to resolve long-term dependencies and co-reference within the context
上下文表示通过self-attention(Cheng等人,2016)来解决上下文中的长期依赖和共同引用。
-
这一层的输入是上一层的最终的reasoning cell ck
-
我们首先通过一个全连接层, 然后加上一个双向LSTM来获取另一个背景cSA的代表
-
获取了c’
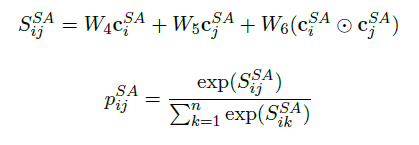

self-attention的输出是由双向LSTM的另一层产生
-
finally, we add this residually to ck to obtain the encoded context c = ck + c‘’.
最后,我们将该残差添加到CK以获得编码的上下文C。
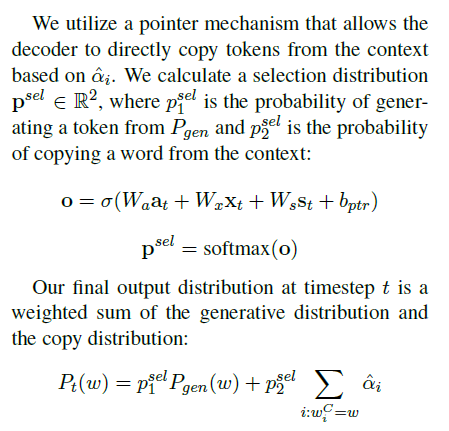
pointer_generater Decoding layer
-
a attention-pointer-generator decoder (see et al., 2017) that attends on and potentially copies from the context is used to create the answer.
关注 attention-pointer-generator解码器(参见等人,2017)用于创建答案,并可能从上下文中复制。
-
生成答案

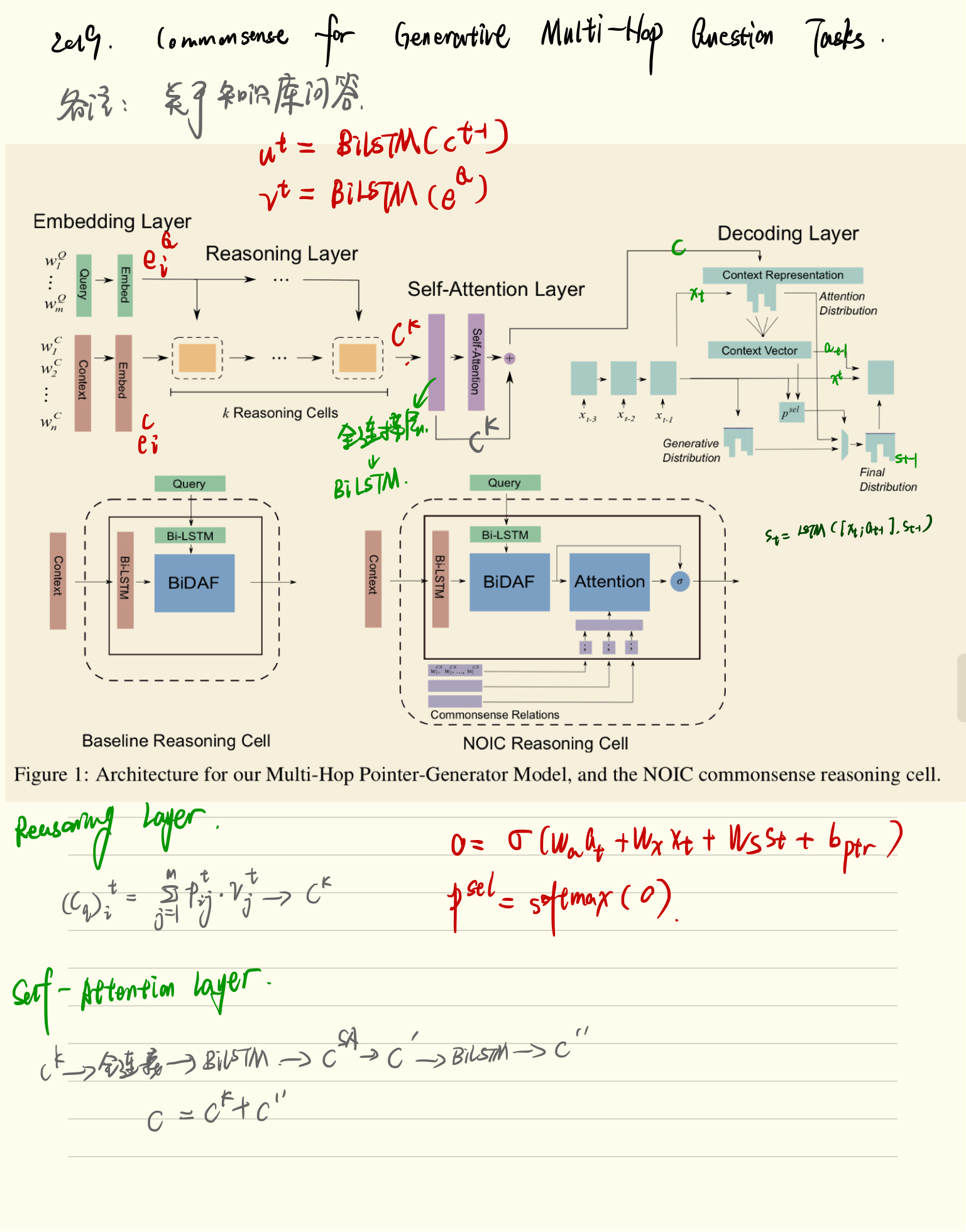
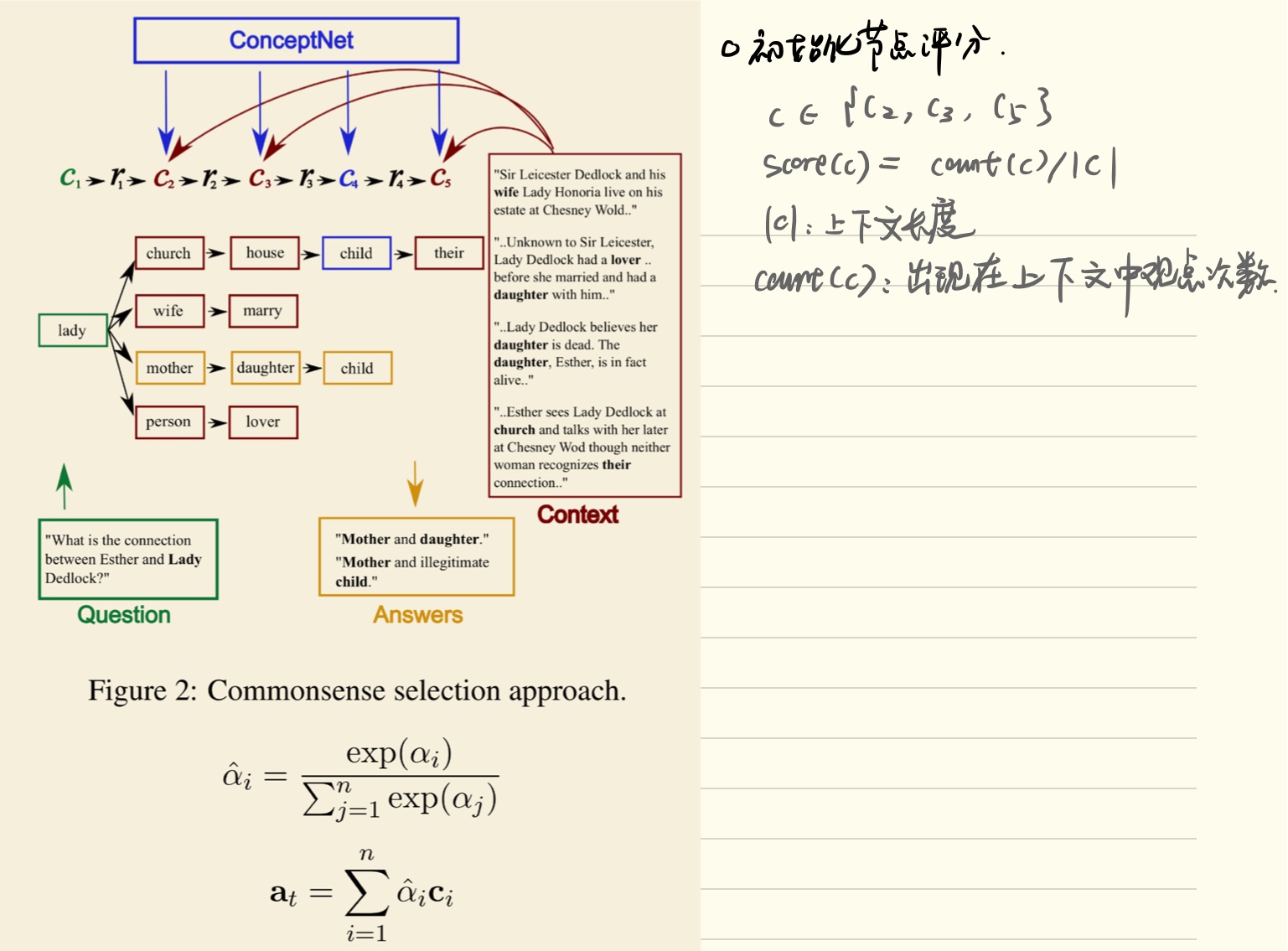
Commonsense Selection and Representation
-
in qa tasks that require multiple hops of reasoning, the model often needs knowledge of relations not directly stated in the context to reach the correct conclusion. in the datasets we consider, manual analysis shows that external knowledge is frequently needed for inference (see table 1).
在需要多次跳转推理的QA任务中,模型往往需要对上下文中没有直接陈述的关系的知识才能得出正确的结论。在我们考虑的数据集中,手工分析表明,推断经常需要外部知识(见表1)。
-
概念之间总是有细微差距, 当推理一个问题时,采取正确的这些概念
-
even with a large amount of training data, it is very unlikely that a model is able to learn every nuanced relation between concepts
即使有大量的培训数据,模型也不太可能了解概念之间的每一个细微关系。
-
从ConceptNet中引入的关系,来补救信息
-
we remedy this issue by introducing grounded commonsense (background) information using relations between concepts from ConceptNet (speer and havasi, 2012)1 that help inference by introducing useful connections between concepts in the context and question.
我们通过引入基于常识(背景)的概念之间的关系来纠正这一问题,通过在上下文和问题中引入概念之间的有用联系来帮助推断。
- 我们需要一个有效的方法来选择关系,这些提供了异常的信息
- 通过构造树的方法
- 标记和过滤这些路径来确保添加信息的质量和多样性,通过三步走的得分策略(初始化结点得分)累计结点得分,进行路径选择。
Tree Construction
-
给定上下文C和问题Q
-
we want to construct paths grounded in the pair that emulate reasoning steps required to answer the question.
我们希望构建基于对的路径,以模拟回答问题所需的推理步骤。
-
in this section, we build ‘prototype’ paths by constructing trees rooted in concepts in the query with the following branching steps3 to emulate multihop reasoning process.
在本节中,我们通过构建基于查询中概念的树来构建“原型”路径,并通过以下分支步骤3来模拟多跳推理过程。
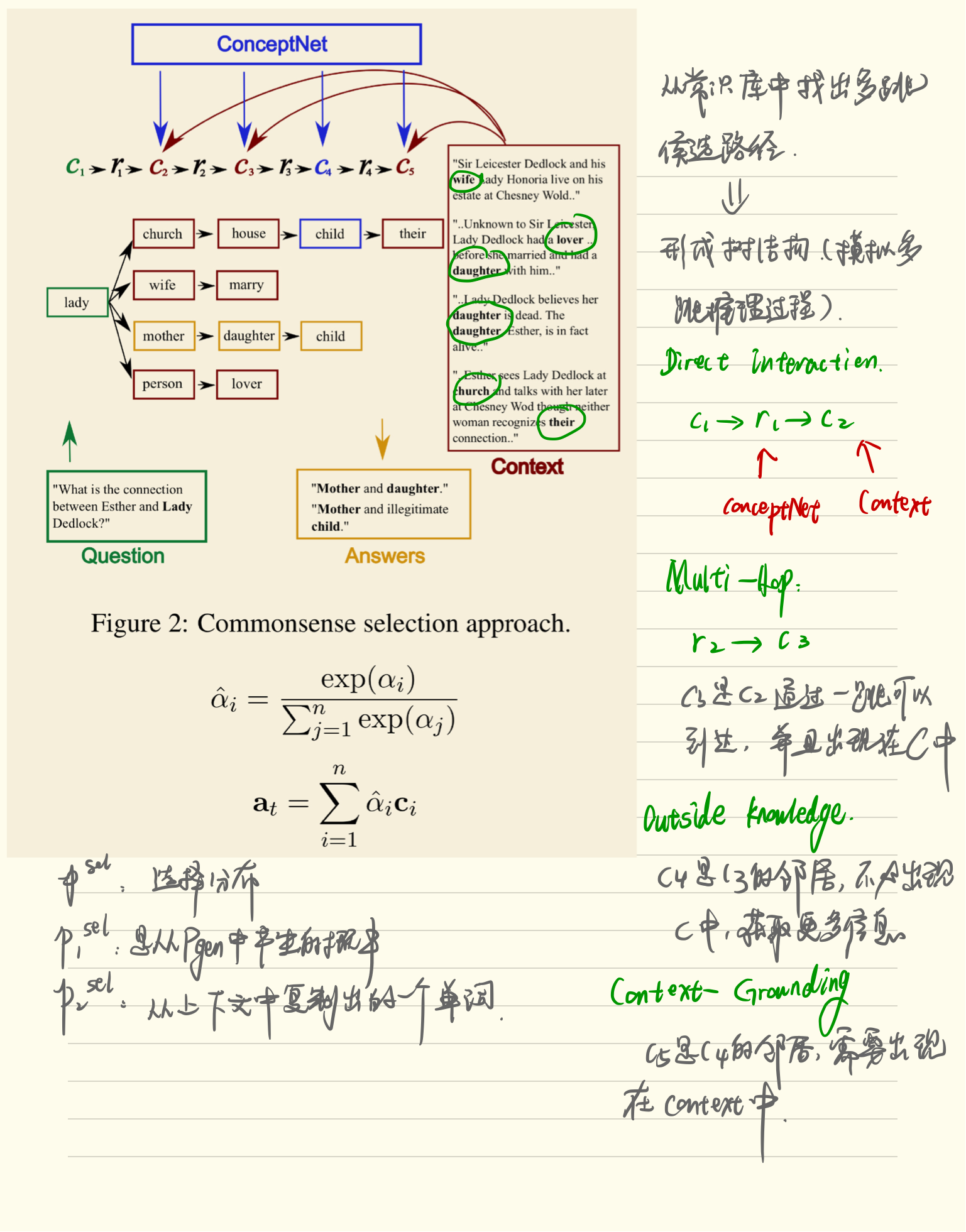
Direct Interaction
- 从ConceptNet中选择r1, 直接连接c1
- lady—> church, lady —> mother, lady!—>person
Multi - Hop
- 从ConceptNet中选择r2, 连接c2到另一个概念c3
- 模仿一个潜在的推理跳转在MRC任务中
Outside Knowledge
-
允许一个不受约束的跳跃到c3的邻居
-
this emulates the gathering of useful external information to complete paths within the context
这将模拟收集有用的外部信息以完成上下文中的路径。
context-grounding
环境-接地
- 为了确保外部的知识对于该任务是真正有帮助的,显示连接第二维度
Rank and Filter
- 树的构造可以收集大量的潜在,相关或者有用的数据, 但是同时这些步骤也可能会引入噪声, 得到和问题不相关的答案
- 所以,引入3步走的得分方法
Initial Node Scoring
- 为了提供最有用的常识
可待挖掘的亮点
- 论文的一个亮点,是使用常识信息进行推理,针对的问题是阅读理解中的问答,也即给定一个问题, 要给出相应的答案;
- 提出来一套常识的选择和表示机制,可以借鉴;
- 论文中的数据是英文的,而如果我们是针对法律领域的数据的,可以进一步利用词性,句法语义分析;
- 如果是针对法律领域的应用场景,如果是针对问答的题目,设定一个法律文书的Context,或者多个Context,利用论文中的多跳推理, 结合创建出的法律文书的知识图谱,结合使用,给出最后的答案;
- 论文中使用的模型是RNN+attention+Pointer,模型的地方也可以进一步进行改进,换个模型?比如RNN的模型换成GRU或者其他,attention这边采用其他attention。





