Jie Mei, Aminul Islam, Abidalrahman Moh’d, Yajing Wu, Evangelos E. Milios: Statistical learning for OCR error correction. Inf. Process. Manage. 54(6): 874-887 (2018)
问题备注
-
OCR后处理
-
OCR矫正
### 摘要
-
modern ocr engines incorporate some form of error correction, typically based on dictionaries. however, there are still residual errors that decrease performance of natural language processing algorithms applied to ocr text
现代OCR引擎结合了某种形式的纠错,通常基于字典。然而,仍然存在一些残差,降低了应用于ocr文本的自然语言处理算法的性能。
-
in this paper, we present a statistical learning model for postprocessing ocr errors, either in a fully automatic manner or followed by minimal user interaction to further reduce error rate
本文提出了一种后处理OCR错误的统计学习模型,该模型要么以完全自动的方式处理,要么以最小的用户交互来进一步降低错误率。
-
our model employs web-scale corpora and integrates a rich set of linguistic features.
我们的模型采用了网络规模的语料库,并集成了一组丰富的语言特征。
-
through an interdependent learning pipeline, our model produces and continuously refines the error detection and suggestion of candidate corrections.
通过一个相互依赖的学习过程,我们的模型产生并不断完善了候选修正的错误检测和建议。
-
evaluated on a historical biology book with complex error patterns, our model outperforms various baseline methods in the automatic mode and shows an even greater advantage when involving minimal user interaction.
在一本具有复杂错误模式的历史生物学书籍上,我们的模型在自动模式下优于各种基线方法,并且在涉及最少用户交互时显示出更大的优势。
-
quantitative analysis of each computational step further suggests that our proposed model is well-suited for handling volatile and complex ocr error patterns, which are beyond the capabilities of error correction incorporated in ocr engines
对每个计算步骤的定量分析进一步表明,我们提出的模型非常适合于处理包含在OCR引擎中的纠错能力之外的易失性和复杂OCR错误模式。
方法
- 使用丰富的语料库,结合丰富的语义特征集合
-
通过互相依存的学习管道,模型可以产生连续的错误检测和候选矫正的建议。continuously refines the error detection and suggestion of candidate corrections.不断完善误差检测和候选修正的建议。
-
in our ocr post-processing model, we design the entire correction pipeline to handle ocr-specific error patterns
在我们的ocr后处理模型中,我们设计了整个校正管道来处理ocr特定的错误模式。
- 为了处理含噪OCR文本中的歧义词边界,提出了一种两阶段标记化方案,该方案首先利用词汇表进行模糊边界检测,然后采用Peen树库约定对标记进行规范化。
Introduction
介绍了一下,目前OCR识别上面存在的一些问题
OCR识别出来的作物更复杂
使用标准的引用规则难以正确处理
对于手写体以及类别错误,违反了Damerau–Levenshtein edit operations 的组合
OCR的识别错误会来自各种各样的背景因素,包括算法缺陷(比如说分词,分类的准确性), 硬件条件的限制(低质量的扫描设备),复杂的内容(文本字体的混合多样性,复杂的页面排版)
它因此导致了不稳定的错误模式
-
ongoing effort on large-scale digitization has made a massive amount of printed information available to search, access, and analyze. besides some well-known internet archives, such as google books,1 biodiversity heritage library,2 and project gutenberg,3 digitization has been actively organized by public institutions covering a wide range of documentation including historical archives, medical reposts, and government document repositories.
正在进行的大规模数字化工作使大量印刷信息可用于搜索、访问和分析。除了google图书、1个生物多样性遗产图书馆和Gutenberg项目等一些著名的互联网档案外,公共机构还积极组织了3次数字化活动,涵盖了包括历史档案、医疗转寄和政府文献储存在内的广泛文件。
-
however, poor optical character recognition (ocr) accuracy is the primary issue that affects the presentation and analytics of the digitized texts (alex & burns, 2014; lam-adesina & jones, 2006; lopresti, 2009; reynaert, 2014; thompson et al., 2016).
然而,光学字符识别(Opr)的准确性差是影响数字化文本的表示和分析的主要问题(Alex)。
-
it is especially problematic for documents that require high reliability, such as medical information (thompson, mcnaught, & ananiadou, 2015) and government records (pereda & taghva, 2011).
对于需要高可靠性的文件,如医疗信息,它特别成问题(Thompson,McNaught,
-
however, the scanned image files have different qualities, layouts, and font types which introduce errors that may be hard to avoid in a unified ocr workflow that aims for both efficiency and generality. also, ocr engines that typically apply dictionary-based validation method has limited correction capability (smith, 2007).
但是,扫描后的图像文件具有不同的质量、布局和字体类型,这些错误在统一的OCR工作流中是很难避免的,其目的是提高效率和通用性。此外,通常应用基于字典的验证方法的OCR引擎的校正能力有限(Smith,2007)。
-
ocr post-processing is the procedure that aims to fix the residual errors in the ocr-generated text. the general practice of postprocessing error correction on the ocr-generated text is agnostic to ocr engines and in the absent of the original scanned document image.
OCR后处理是一种旨在修复OCR生成文本中残留错误的过程.对OCR生成的文本进行后处理错误校正的一般做法与OCR引擎无关,在没有原始扫描文档图像的情况下也是如此。
-
an ocr post-processing model is thus able to be applied to digitized texts or a digitization pipeline with any ocr engine. ocr post-processing techniques has been broadly researched for manuscripts of different languages
因此,OCR后处理模型可以应用于具有任何OCR引擎的数字化文本或数字化管道。摘要OCR后处理技术对不同语言的手稿进行了广泛的研究。
-
given only ocr-generated text as input, ocr error correction is arguably similar to correcting spelling errors
仅以ocr生成的文本作为输入,ocr错误更正可以说与更正拼写错误类似。
-
conversely, ocr errors are inherently more volatile and complex than the misspellings generated by humans
相反,与人类产生的拼写错误相比,OCR错误本质上更易变,也更复杂。
-
the error patterns are usually being understood by the combination of damerau–levenshtein edit operations. however, a large portion of ocr errors violate such one-to-one character modification
错误模式通常是由damerau-levenshtein编辑操作的组合来理解的。然而,很大一部分ocr错误违反了这种一对一的字符修改。
-
noisy text tokenization is known to have issues in word boundary detection
摘要噪声文本标记在词边界检测中存在问题。
-
tokenization schemes using space and punctuation inevitably lead to merging (e.g., ofthe) and splitting (e.g., j ust or typir,al) errors
使用空间和标点符号的标记化方案不可避免地导致合并(例如,of)和分裂(例如j、ust或type ir,al)错误。
-
to deal with ambiguous word boundaries in noisy ocr text, we propose a two-stage tokenization scheme, which first utilizes a vocabulary to assert fuzzy boundary detection, and then adopts peen treebank conventions to normalize tokens.
为了处理含噪OCR文本中的歧义词边界,提出了一种两阶段标记化方案,该方案首先利用词汇表进行模糊边界检测,然后采用Peen树库约定对标记进行规范化。
-
the quantitative analysis of feature importance shows that n-gram context is important for error detection and a combined effort from different feature types is necessary for correction.
对特征重要性的定量分析表明,n-gram背景对于误差检测是重要的,并且需要来自不同特征类型的组合努力进行校正。
-
为了提高查找更正错误模式的机会,使用两种方法在Google Web IT 预料库中探索候选集
贡献
-
we employ a tokenization scheme that can better deal with the boundary ambiguity to reduce the tokenization errors propagated into the downstream processes
我们采用一种可以更好地处理边界模糊的标记化方案,以减少传播到下游过程的标记化误差。
-
for error detection, our model first reduces misidentified errors using a recall-oriented classifier, and then increases the detection accuracy by filtering the false predicted errors
对于错误检测,我们的模型首先使用面向召回的分类器来减少错误识别的错误,然后通过过滤错误预测的错误来提高检测的准确性。
-
our model effectively locates correction within a very small candidate set by extensively exploring candidates in web-scale n-gram corpora and pruning them with linguistic features.
我们的模型有效地定位在一个非常小的候选集内,通过在网络规模的n-gram语料库中对候选对象进行广泛的探索,并根据语言特征对它们进行剪枝。
-
we show that high quality suggestion can be achieved by leveraging diversified linguistic features using an ensemble regressor, which is robust to handle different scenarios including complex errors and false predicted errors.
我们表明,利用集合回归器可以利用多种语言特征来获得高质量的建议,它对处理复杂错误和错误预测错误等不同场景具有很强的鲁棒性。
-
the evaluation on post-processing an ocr-generated historical biology text demonstrates that our proposed correction model outperforms existing models in both its automatic mode (which selects the top suggestion as the correction) and its user-interactive mode (which presents a short list of suggestions to the user from which to select the correction). we conduct quantitative analysis to evaluate the error correction performance of the proposed post-processing pipeline. finally, we discuss potential future directions for improving this model
对OCR生成的历史生物文本的后处理评价表明,我们提出的修正模型在自动模式(选择顶部建议作为校正)和用户交互模式(向选择更正的用户提供了简短的建议列表)方面都优于现有模型。对所提出的后处理流水线的纠错性能进行了定量分析.最后,讨论了改进该模型的未来发展方向。
-
after pretrained by sufficient amount of data, our model is applicable for correcting documents with the same word distribution (i.e.,in the same domain as the training data) and error distribution (i.e.,generated from the same ocr engine). as our model achieves good performance and requires no additional human error in automatic correction, it is well-suited for large-scale digitization.
在经过足够数量的数据预处理后,该模型适用于具有相同单词分布(即与训练数据相同的域中)和错误分布(即从同一个OCR引擎生成)的文档的校正。由于该模型具有良好的性能,在自动校正中不需要额外的人为误差,因此非常适合大规模数字化。
相关工作
-
OCR的后处理模型,根据自动化的程度可以被分类为人工,半自动,自动。
-
大多数的OCR后处理方法,都是来源于拼写矫正的方法
-
人工进行后处理,依赖大量的人工努力
-
自动模型:基于规则结合语义;对于相同的输入图片,选择最好的识别结果,作为最终的输出
-
结合不同OCR引擎的互补的识别结果,可以有一个很好的
-
another type of automatic models leverage linguistic features in an supervised predictor for error detection and correction
另一类自动模型利用监督预测器中的语言特征进行错误检测和校正。
-
Bassil and Alwani (2012). 提出了利用Google Web, 一元语料库作为检测,5-gram语料库,作为纠正
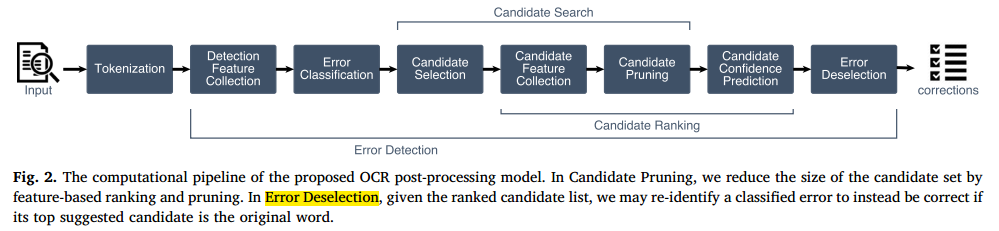
所用模型
-
传统的错误纠正流程,包括三个语句部分:1,来自文本中的错误检测;2,检测误差的候选矫正生成;3,候选排名
-
our proposed model follows this paradigm and implements these phases in an interdependent process
我们提出的模型遵循这个范例,并在一个相互依赖的过程中实现这些阶段。
标记tokenization
-
in ocr-generated text, intra-word characters can be misrecognized as punctuation, which is hard to disambiguate with true punctuation and thus lead to higher token boundary ambiguities
在ocr生成的文本中,单词内字符可能被误认为标点符号,这很难用真正的标点符号来消除歧义,从而导致更高的标记边界歧义。
-
to better handle these two objectives, we follow fares, oepen, and zhang (2013) to separate tokenization into boundary detection and text normalization. we first segment text into subsequences by whitespace characters and then normalize each subsequence following algorithm 1
为了更好地处理这两个目标,我们按照fares、Oepen和Zhang(2013)将标记化分为边界检测和文本规范化。我们首先通过空格字符将文本分割成子序列,然后按照算法1对每个子序列进行规范化。
-
实验给出n-gram标记,并且包含额外的规则,处理特殊的标记
检测特征集
-
负责识别错误标记
-
从以下四种类型的特征中推断标记的正确性
-
单词的有效性
-
字符是否存在
-
准确的语境连贯;一个正确的单词,应该在它的上下文中是连贯的。
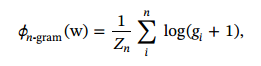
-
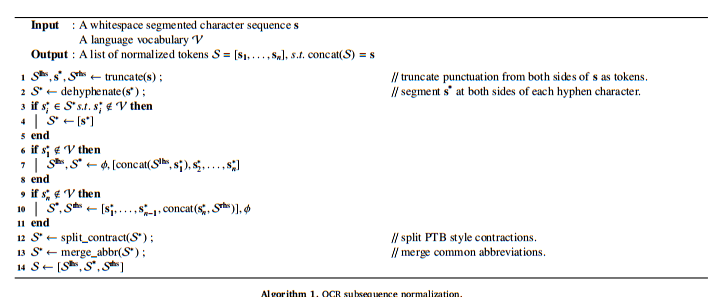
近似语境连贯
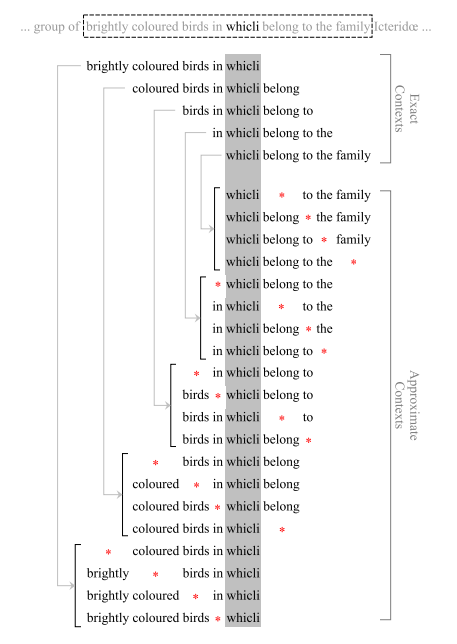
-
错误分类
- 给定一个标记好的文本,分类器必须能够分类出OCR错误的情况,考虑到错误的单词都不会在错误的句子中进行处理,所以,最初该分类器的目标是降低错误
候选集选择
- 为了在候选集中包含负责的错误模式,我们采纳了两种选择的不同方法
候选特征集合
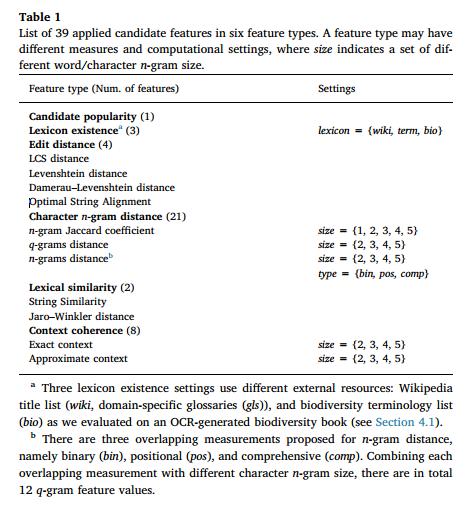
- 呈现了每一个候选的集合,总结了6种特征类型
候选集修剪
-
to broadly represent the word characteristics and their relation with the error, we profile each selected candidate by a vector of linguistic statistics in the following six feature types, where a full list of 39 feature values are shown in table 1
为了广泛地表示单词的特征及其与错误的关系,我们使用以下六种特征类型的语言统计向量对每个选定的候选对象进行了描述,其中包含39个特征值的完整列表如表1所示。
候选置信度预测
-
we adopt a regressor to leverage the candidate features for ranking in the pruned candidates set. to train this regressor, we follow our previous described steps to detect and search candidates for the potential errors in the training text. we then assign binary label to each candidate, where only the correct candidates are labeled as 1, and the union of all candidate set is used for training. since a correct word can be misclassified as an error, we label its original word to 1 if it is included in the suggested candidate set.
我们采用了一个回归器来利用候选特征在修剪后的候选集合中的排名。为了训练这个回归者,我们遵循前面描述的步骤来检测和搜索培训文本中潜在的错误。然后,我们为每个候选人分配二进制标签,其中只有正确的候选人被标记为1,并且所有候选集合的联合用于培训。由于一个正确的单词可能被错误分类为错误,如果它包含在建议的候选集合中,我们将它的原始单词标记为1。
错误取消选择
-
given recall oriented error classification, there are more fp predictions being generated, which will increase human labor in an interactive correction setup.
在面向召回的错误分类中,会产生更多的FP预测,这将增加交互校正设置中的人工。
-
to revise this detection bias, we rejudge the suggested corrections.
为了修正这一检测偏差,我们重新判断所建议的修正。
-
given candidate corrections suggested by the model, an error word is relabeled as correct if its top ranked candidate is the original word
给定模型所建议的候选人更正,如果错误词的顶级候选词是原始单词,则将其重新命名为正确。
实验评估
数据
-
网络规模的语料库
- 实验基于基于一个历史的生物书有着复杂的错误模式
-
the book titled “Birds of Great Britain and Ireland (Volume II, 1907, 274 pages)
-
it is hard to directly compare a new ocr post-processing model with the existing models because the benchmark testing datasets mentioned in the literature are not publicly available.
由于文献中提到的基准测试数据集不是公开的,所以很难将新的OCR后处理模型与现有的模型进行直接比较。
-
we thus created a dataset for ocr post-processing evaluation and made it publicly available
因此,我们为ocr后处理评估创建了一个数据集,并将其公之于众。
-
we manually correct the text to generate the ground truth and list all the ocr errors with their corrections.
我们手动更正文本以生成基本真相,并列出所有OCR错误及其更正。
实验设置
-
80%训练,20%测试
-
该篇文章的所有实验,use English Wikipedia titles as the vocabulary and Google Web 1T dataset as the ngram corpus
-
we thus use the learned classifier to predict errors in the training tokens and use the predicted errors to train a gradient boosting regressor for candidate ranking
因此,我们使用学习到的分类器来预测训练标记中的错误,并利用预测的误差来训练一个梯度增强回归器来进行候选排序。
性能评估
-
precision (Prec.), recall (Rec.), and F1 measure
-
noisy channel is a widely used probabilistic correction model, where suggestions are based on the probability of edit operations between candidates and errors. we adopt the implementation and pretrained dataset given by segaran and hammerbacher (2009
噪声信道是一种广泛应用的概率校正模型,它是基于候选和错误之间编辑操作的概率。我们采用Segaran和Hammerbach(2009)给出的实现和预培训数据集。
矫正案例研究
结论
- 在自动模式下,我们的模型由于各种基线方法, 并且再涉及最少的用户交互时,显示出更大的优势。
启发
- 丰富发语料库
- 矫正管道
- 边界模糊的标记化方法





