b站上一个例子:
数据集
2 1 0 2 2 0 5 4 1 4 5 1 2 3 0 3 2 0 6 5 1 4 1 0 6 3 1 7 4 1
step1:加载文件
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#def loaddata
def loaddata(filename):
file = open(filename)
x = []
y = []
for line in file.readlines():
line = line.strip().split()
x.append([float(line[0]), float(line[1])])
y.append(float(line[-1]))
#将列表格式变成为矩阵的格式
xmat = np.mat(x)
ymat = np.mat(y)
file.close()
return xmat, ymat
#implement
xmat, ymat = loaddata('ytb_lr.txt')
print('xmat:', xmat, xmat.shape)
print('ymat:', ymat, ymat.shape)
运行结果:
D:\1b\Anoconda\setup\set\python.exe E:/python_workspace/ML/WuEnDa_Work/LogisticReg0801.py
xmat: [[ 2. 1.]
[ 2. 2.]
[ 5. 4.]
[ 4. 5.]
[ 2. 3.]
[ 3. 2.]
[ 6. 5.]
[ 4. 1.]
[ 6. 3.]
[ 7. 4.]] (10, 2)
ymat: [[ 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1.]] (1, 10)
step2:定义具体的计算部分
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#def loaddata
def loaddata(filename):
file = open(filename)
x = []
y = []
for line in file.readlines():
line = line.strip().split()
x.append([1, float(line[0]), float(line[1])])
y.append(float(line[-1]))
#将列表格式变成为矩阵的格式
xmat = np.mat(x)
ymat = np.mat(y).T
file.close()
return xmat, ymat
# w calc
def w_calc(xmat, ymat, alpha= 0.001, maxIter = 10001):
# W需要进行一个初始化看,就是里面的参数,初始化为三行一列
W = np.mat(np.random.randn(3,1))
# W update
for i in range(maxIter):
H = 1/(1+np.exp(-xmat*W))
dw = xmat.T * (H - ymat) #dw(3, 1)
W -= alpha * dw
return W
#implement
xmat, ymat = loaddata('ytb_lr.txt')
# print('xmat:', xmat, xmat.shape)
# print('ymat:', ymat, ymat.shape)
W = w_calc(xmat, ymat)
print(W)
运行结果:
D:\1b\Anoconda\setup\set\python.exe E:/python_workspace/ML/WuEnDa_Work/LogisticReg0801.py
[[-5.62068929]
[ 0.71391472]
[ 0.69674633]]
step3:图像展示
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#def loaddata
def loaddata(filename):
file = open(filename)
x = []
y = []
for line in file.readlines():
line = line.strip().split()
x.append([1, float(line[0]), float(line[1])])
y.append(float(line[-1]))
#将列表格式变成为矩阵的格式
xmat = np.mat(x)
ymat = np.mat(y).T
file.close()
return xmat, ymat
# w calc
def w_calc(xmat, ymat, alpha= 0.001, maxIter = 10001):
# W需要进行一个初始化看,就是里面的参数,初始化为三行一列
W = np.mat(np.random.randn(3,1))
# W update
for i in range(maxIter):
H = 1/(1+np.exp(-xmat*W))
dw = xmat.T * (H - ymat) #dw(3, 1)
W -= alpha * dw
return W
#implement
xmat, ymat = loaddata('ytb_lr.txt')
# print('xmat:', xmat, xmat.shape)
# print('ymat:', ymat, ymat.shape)
W = w_calc(xmat, ymat, 0.001, 50000)
print(W)
# show
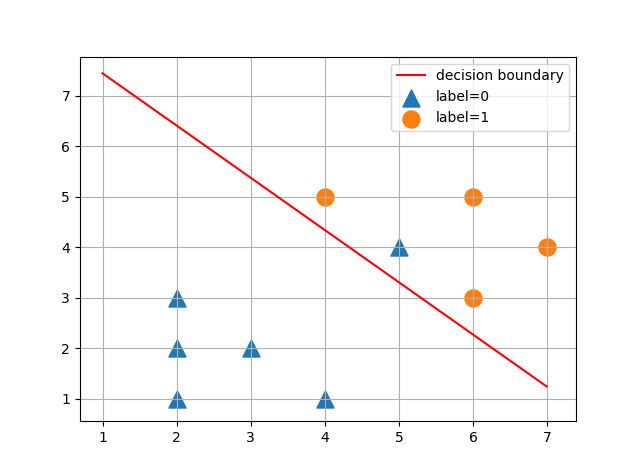
#分界线也需要画出来
w0 = W[0,0]
w1 = W[1,0]
w2 = W[2,0]
plotx1 = np.arange(1, 7, 0.01)
plotx2 = -w0/w2 - (w1/w2)*plotx1
#线条画出来
plt.plot(plotx1, plotx2, c='r',label='decision boundary')
#每个点显示出来;.A表示变成array的形式
plt.scatter(xmat[:, 1][ymat==0], xmat[:, 2][ymat==0].A, marker='^', s=150, label='label=0')
plt.scatter(xmat[:, 1][ymat==1], xmat[:, 2][ymat==1].A, s=150, label='label=1')
#网格线
plt.grid()
#图标
plt.legend()
plt.show()
运行结果:
step4:图的动态呈现
在之前代码的基础上进行修改
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#def loaddata
def loaddata(filename):
file = open(filename)
x = []
y = []
for line in file.readlines():
line = line.strip().split()
x.append([1, float(line[0]), float(line[1])])
y.append(float(line[-1]))
#将列表格式变成为矩阵的格式
xmat = np.mat(x)
ymat = np.mat(y).T
file.close()
return xmat, ymat
# w calc
def w_calc(xmat, ymat, alpha= 0.001, maxIter = 10001):
# W需要进行一个初始化看,就是里面的参数,初始化为三行一列
W = np.mat(np.random.randn(3,1))
#需要把每一步记录下来
w_save = []
# W update
for i in range(maxIter):
H = 1/(1+np.exp(-xmat*W))
dw = xmat.T * (H - ymat) #dw(3, 1)
W -= alpha * dw
#每100步记录一下
if i%100 == 0:
#如果不加copy,存的永远是最后一个数
w_save.append([W.copy(),i])
return W, w_save
#implement
xmat, ymat = loaddata('ytb_lr.txt')
# print('xmat:', xmat, xmat.shape)
# print('ymat:', ymat, ymat.shape)
W, w_save = w_calc(xmat, ymat, 0.001, 10000)
print('W:', W)
# show
#分界线也需要画出来
for wi in w_save:
#如果不加clf,每一个轨迹都会保存下来,不是很好看
plt.clf()
#因为wi有两个数
w0 = wi[0][0,0]
w1 = wi[0][1,0]
w2 = wi[0][2,0]
plotx1 = np.arange(1, 7, 0.01)
plotx2 = -w0/w2 - (w1/w2)*plotx1
#线条画出来
plt.plot(plotx1, plotx2, c='r',label='decision boundary')
#每个点显示出来;.A表示变成array的形式
plt.scatter(xmat[:, 1][ymat==0], xmat[:, 2][ymat==0].A, marker='^', s=150, label='label=0')
plt.scatter(xmat[:, 1][ymat==1], xmat[:, 2][ymat==1].A, s=150, label='label=1')
#网格线
plt.grid()
#图标
plt.legend()
#有这个命令就可以生成动画
plt.title('iter:%s'%np.str(wi[1]))
plt.pause(0.001)
#如果不加show,最后执行完就会消失
plt.show()





